The crustaceans they are arthropod animals. They are mainly aquatic, both freshwater and saltwater. For instance: water flea, krill, lobster.
Classification of crustaceans:
- Class Branchiopoda. They have appendages in the cephalic region in the form of a sheet, divided into lobes and with a small branchial sheet on the outside.
- Remipedia class. They are worm-shaped, have no eyes, and are transparent white. They live in groundwater and are small, reaching up to 3 mm in length.
- Class Cephalocarida. They are only ten species of size between 2 and 4 millimeters in length. They do not have eyes, with the long body compressed in the cephalic area.
- Class Maxillopoda. They have a reduced abdomen and appendages.
- Class Ostracoda. Some species are microscopic and the largest are 2 mm. They have a two-valve shell that can be soft or rigid due to calcification, covering the soft parts of the animal.
- Malacostraca class. They are the group with the largest number of crustaceans, having more than 42 thousand known species.
Characteristics of crustaceans

- Articulated exoskeleton: a shell protects the body.
- They generally have 5 pairs of legs, two pairs of antennae, and one pair of jaws.
- Body divided into:
- Cephalothorax: fusion of head and thorax
- Abdomen: formed by articulated segments
- In general they have oviparous reproduction, with external fertilization.
Examples of crustaceans
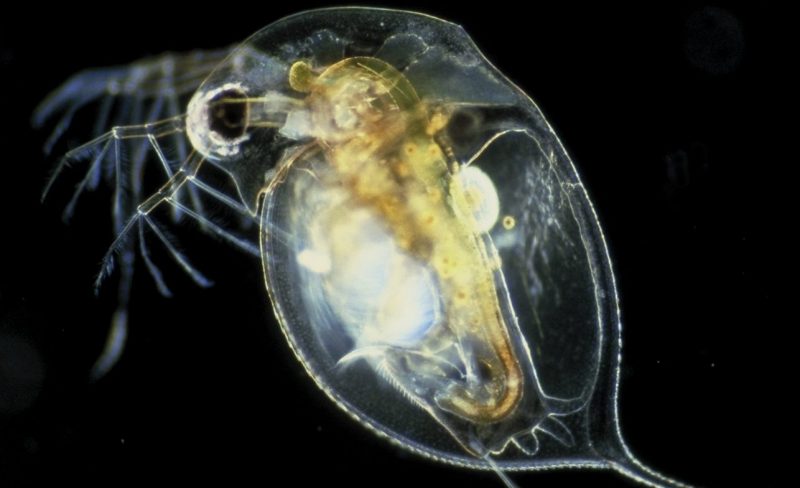
- Water flea (daphnia). Planktonic crustacean. When they swim, they seem to jump, which is why they are called fleas. They feed on microorganisms and phylloplankton.
- Artemias. Gill crustaceans. They live in salt water and remain almost unchanged in evolution since the Triassic period.
- Barnacles. They grow on rocks on which the waves fall. It has no limbs and remains immobile attached to the rocks. It is fed by filtration of the nutrients that the waves bring.
- Krill. Malacostraceous crustaceans. Its appearance is externally similar to shrimp, having lengths between 3 and 5 cm in length. It feeds on phylloplanct and in turn is food for many Antarctic species.
- Galley. Stomatopod crustacean. It is used in gastronomy, but it is not very appreciated due to the small amount of meat it contains.
- Balanus (sea acorns). Barnacles crustaceans. They are usually found in shallow coastal areas, on rocks, shells of other animals, poles and any object found on the coast. They are covered by a grayish shell.
- Prawns. Decapod crustaceans. They live in both fresh and salt water. They are very popular in gastronomy.
- Pea crab. It is a very small crab that is introduced into bivalve mollusks (oysters, clams, mussels) and lives parasitically on the food consumed by mollusks.
- Whale lice (cyamidae). An external parasite that is associated with cetaceans, such as whales. It is located in the skin lesions of cetaceans, as well as in their folds and eyes.
- Locust. Decapod crustacean, highly appreciated in culinary terms. They live on rocky bottoms where they seek shelter and, to get around, they can swim or walk.
